[Mách Bạn] phương pháp giải bài toán tổng tỉ – hiệu tỉ dễ dàng – Đại
Chào mừng bạn đến với pgdgiolinhqt.edu.vn trong bài viết về Mach ban phuong phap giai bai toan tong ti hieu ti de dang chúng tôi sẽ chia sẻ kinh nghiệm chuyên sâu của mình cung cấp kiến thức chuyên sâu dành cho bạn.
[Mách Bạn] easy method to solve the problem of total billion – difference of billions
The problem of the sum of billions – the difference or more fully is the problem of finding two numbers when the sum and ratio of that number is known and the problem of finding two numbers when knowing the difference and ratio of that number the student has learned in the chapter. Math 4, elementary level.
This is a good math problem and quite difficult for students. To be able to distinguish which problems are in the form of sum-to-billions and which ones are in the form of sum-to-billions, not all students can easily grasp them. Today’s article, Trinh Hoai Duc High School will tell you some really good methods!

I. MATH FORM TOTAL – BILLION
1. Steps to solve the Sum – Ratio problem
Step 1: Find the sum of two numbers (if the sum is hidden)
Step 2: Find the ratio (if the ratio is unknown)
Step 3. Draw a diagram based on the given data.
Step 4. Find the total number of equal parts
Step 5. Find small and large numbers (You can find big numbers first or find them later and vice versa
Small number = (Sum: equal parts) x number of parts of small number (Or Sum – large number)
Large number = (Sum: equal parts) x number of parts of large number (Or sum – small number)
Step 6. Conclusion Answers
(Students can take an extra step of retrying to verify their results.)
2. Special circumstances
The multi-problem problem does not give complete data about sums and ratios, but can give the following data:
- Missing (hidden) total (Indicates score, does not give total)
- Missing (hidden) billion (Indicate total, do not give score)
- For the data to add, subtract numbers, create a total (billion) to find the original number.
For problems with such data, it is necessary to make an extra step back to the basic problem. In the following article, I will guide each of these special cases in detail. Remember to follow!
Example of the sum-billion problem
A rectangle has a perimeter of 460 cm. Calculate the width and length of that rectangle knowing that the length is 4 times the width.
Solution steps:
Step 1: Find the sum of two numbers
The problem says that the perimeter of the rectangle is 460 cm. However, to find the length and width of the rectangle, we have to find the half circumference (divide the circumference by 2).
Step 2: Find the ratio: The length is 4 times the width, that is, for the ratio ¼, ie the width (small number) is 1 part and the length (large number) is 4 equal parts.
Step 3: Draw the diagram
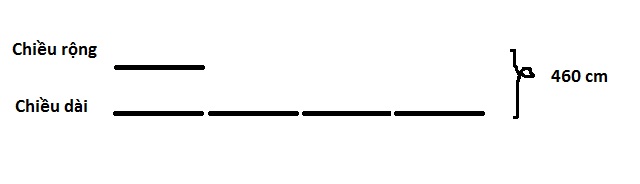
Step 4: Find the total number of equal parts:
Looking at the diagram, we see that the width is 1 part, the length is 4 parts and the total length + width (total equal parts) = 5 parts.
Step 5: Find the small number value (width), the large number value (length)
Step 6: Answer and try again
Solution:
Half perimeter of rectangle is: 460 : 2 = 230 (cm)
Looking at the diagram we see that the total number of equal parts is: 5 + 1 = 5
The length of the rectangle is: 230 : 5 x 4 = 184 (cm)
The length of the rectangle is: 230 : 5 x 1 = 46 (cm)
Answer: length: 180cm and width: 46cm
Retry:
We see 46/184 = 1/4
Perimeter of the rectangle is: (184 + 46) x 2 = 460 (cm) satisfying the proposition.
3. Application exercises
Lesson 1: Two numbers whose sum is 7030 and their ratio is 53 and 21. Find the smaller number.
Solution:
The total number of equal parts is:53 + 21 = 74 (part)
The small number is:7030 : 74 × 21 = 1995
Answer: 5035
Lesson 2: Lan and Mai have 25 notebooks. Minh’s notebooks are 2/3 of Khoi’s books. How many notebooks does each person has?
Prize
Line diagram
Number of Lan’s notebooks: |—-|—-|
Number of Mai’s notebooks: |—-|—-|—-|
The total number of equal parts is: 2 + 3 = 5 (parts)
Lan’s notebooks are: 25 : 5 x 2 = 10 (notebooks)
Mai’s notebooks are: 25 : 5 x 3 = 15 (notebooks)
Answer: Lan: 10 notebooks
Mai: 15 notebooks
Lesson 3. The sum of two numbers is 72. Find the two numbers, knowing that if the large number is reduced by 5 times, then the small number is obtained.
Comment
– Problem of finding two numbers when the sum and ratio of the two numbers are known.
– The card event is in the form of a hidden score.
Detailed solution
Step 1. Return to basic form
Larger number is 5 times smaller than smaller number => Small number = 1/5 of the big number
Step 2. Draw the diagram
Small number: |—-|
Big numbers: |—-|—-|—-|—-|—-|
Step 3. The number of equal parts is: 1 + 5 = 6
Step 4. Number of babies: 72:6 = 12
Large numbers: 72 : 6 x 5 = 60
Step 5. Answer: Number of children: 12
Large number: 60
4. Practice exercises
Lesson 1: The sum of two numbers is 333. The ratio of two numbers is 2/7. Find two of them.
Lesson 2: Two warehouses hold 125 tons of paddy. The number of paddy in the first barn is equal to 3/2 of the number in the second barn. How many tons of paddy does each storehouse hold?
Lesson 3: A rectangular garden plot has a perimeter of 200 m and its length is 3 times its width. Calculate the area of the garden?
Lesson 4: A rectangular piece of land has a perimeter of 240 m and the width is 2/3 of the length. Calculate the area of that rectangle.
Lesson 5: Find the natural number. Knowing that when we add a zero to the right of that number, we get the new number and the sum of the new and old numbers is 297.
Lesson 6: The average of two numbers is 440. If we add a zero to the right of the small number, we get the large number. Find those 2 numbers.
Lesson 7: Find the natural number. Know that if we add a 2 to the right of that number, we get a new number. The sum of the new and old numbers is 519.
Lesson 8: Find two numbers whose sum is 107. Know that if we remove the digit 8 from the units row of the large number, we get the small number.
Lesson 9: Find natural numbers. We know that when we add the number 52 to the right of that number, we get a new number. The sum of the new number and that number equals 5304.
Lesson 10: The average of 3 numbers is 85. If you add a zero to the right of the second number, you get the first number, if you add four times the second number, you get the third number. Find those 3 numbers.
Lesson 11: The sum of 2 numbers is equal to 385. One of the two numbers ends with zero, if we delete that zero, we get 2 equal numbers. Find two of them.
Lesson 12: A parallelogram has an area of 216 cm2 and the height is 12cm. If the height is doubled and the length is decreased by 6 cm, how will the area of the new rectangle change compared to the area of the original parallelogram?
Lesson 13: The seller has a bag of rice, the first time he sells 3kg, the next time he sells 1/3 of the remaining rice, leaving 18kg. How much did the bag of rice weigh in the beginning?
Lesson 14: The sum of the present ages of father and son is 50 years. Five years later, the father’s age will be 3 times the son’s age. Calculate the age of each person present?
Lesson 15: Uncle Tuan came to visit Uncle Hung’s house. Uncle Hung and Miss Lan sat down to talk. Uncle Hung said to Uncle Tuan: “Day two of us
When she joined the army, Ms. Lan’s age was 1/3 of my age, but now the total age of my two brothers is 48 years old and Ms. Lan’s age is exactly the same as mine when I joined the army.” How old do you think Miss Lan is this year?
Lesson 16: On the occasion of Tet, the store received some jam boxes. Because the counter is tight, the seller only leaves 1/10 of the jam boxes at the counter, the rest is stored inside. After selling 4 boxes at the counter, the number of boxes put away is 15 times more than the number of boxes left at the counter. How many boxes of jam did the store receive at first?
Lesson 17: A cat chases a mouse 3m away from it. Each step the cat jumps 8dm, the mouse jumps 3dm. After how many steps does the cat catch the mouse?
Lesson 18: The present age of the father is 7 times the age of the son. After 10 years, father will be 3 times as old as son. Calculate the age of each person present.
II. MATH FORM – BILLION
1. Steps to solve the Difference – Ratio problem
Step 1: Find the difference of two numbers (if the difference is hidden)
Step 2: Find the ratio (if the ratio is unknown)
Step 3: Draw map
Step 4: Find the difference of equal parts
Step 5 : Find small and large numbers (Can find big numbers first or search later and vice versa
Small number = (Difference: equal parts) x number of parts of small number (Or Difference – big number)
Large number = (Difference: equal parts) x number of parts of large number (Or Difference – small number)
Step 6 : Conclusion of the answer
(Students can take an extra step of retrying to verify their results.)
2. Special circumstances
The multi-problem problem does not give complete data about the difference and ratio, but can give the following data:
- Missing difference (specify score, don’t know difference)
- Missing billion (indicates the difference, not the ratio)
- For the data to add, subtract numbers, create a difference (billion) to find the original number
For problems with such data, it is necessary to make an extra step back to the basic problem. In the following article, I will guide each of these special cases in detail. Remember to follow!
Example problem of Difference – Ratio
The difference of two numbers is 192. The ratio of the two numbers is 3/5. Find two of them.
Step 1: Determine the difference: 192
Step 2: Determine the score: 3/5
Step 3: Draw the diagram

Step 4: Find the difference of equal parts: 5 – 3 = 2 parts
Step 5: Find the value of large and small numbers
Large number: 192 : 2 x 5 = 480
Number of children: 192 : 2 x 3 = 288
Step 6: Answer and try again
We see: 288/480 = 3/5 and 480 – 288 = 192 satisfy all requirements.
3. Application exercises
Lesson 1: The difference of two numbers is 1170 and their ratio is 49 and 4. Find the smaller number.
Solution:
The equal part difference is:49 – 4 = 45 (parts)
The big number is:1378 : 45 × 49 = 104
Answer: 1274
Lesson 2: The difference of two numbers is 4158 and their ratio is 61 and 19. Find the big number.
Solution:
The equal part difference is:61 – 19 = 42 (parts)
The big number is:7920 : 42 × 61 = 1881
Answer: 6039
lesson 3: The length of the rectangle is 3/2 the width. If the width is increased by 20m, the rectangle becomes a square. Calculate the area of the rectangle?
Hint: this is a difference (hidden)-billion problem, because the difference is hidden, you have to find the difference, then apply the usual steps to solve the difference-billion problem.
According to the problem, the difference in length and width is 20m
According to the diagram, the equal part difference is: 3 – 2 = 1 (part)
The length of the rectangle is: 20 x 3 = 60 (m)
The width of the rectangle is : 20 x 2 = 40 (m)
The area of the rectangle is: 60 x 40 = 2 400 (m)
Answer: 2 400 m
4. Practice exercises
Lesson 1: Currently, the mother is 28 years older than the child. Know that 3 years later, the son’s age is 3/7 of the mother’s age. How old is each person now?
Lesson 2: Find two numbers whose difference is 216, knowing that if you add a zero to the right of the smaller number, you get the larger number.
lesson 3: The difference of two numbers is 393, knowing that if you remove the last digit of a large number, you get a small number.
Lesson 4: Find two numbers whose difference is 516, knowing that if the larger number is divided by the smaller, the quotient is 4.
Lesson 5: Find two numbers whose difference is 165, knowing that if the larger number is divided by the smaller, the quotient is 7 and the remainder is 3.
Lesson 6: An HCN has a width of 2/5 of its length. Find the perimeter and area of the rectangle, if the width is increased by 21 cm and the length remains the same, then the HCN becomes a square.
Lesson 7: The HCN plot has a width equal to 3/5 of its length. Assume that if the length is reduced by 9 m and the breadth is increased by 7 m, the plot will be square. Calculate the area of that HCN land?
Lesson 8: Class 4 A planted 18 trees less than class 4B. Knowing that 7 times the number of trees class 4A can grow is 5 times the number of trees class 4 B can grow. Ask how much each class to plant trees ?
Lesson 9: Tung has 20 more marbles than Binh. Knowing that 15 times Binh’s number of marbles is 5 times Tung’s number of marbles. Ask how much each class to plant trees ?
Lesson 10: Class 4 A has 1/3 of the number of boys as 1/5 of the number of girls. The number of female students is 10 more than the number of male students. Find the number of male students and the number of female students?
You have just learned the easiest way to solve the sum of billions – difference of billions problem. Hopefully, the detailed and specific sharing above will help you better master this very important math-solving knowledge. In the following article, we will introduce in detail, specifically each form of sum – billion, difference for you to easily grasp. Don’t miss it!
Posted by: Trinh Hoai Duc High School
Category: General Knowledge
