Lung Cancer: Types, Stages, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Chào mừng bạn đến với pgdgiolinhqt.edu.vn trong bài viết về Lung me chúng tôi sẽ chia sẻ kinh nghiệm chuyên sâu của mình cung cấp kiến thức chuyên sâu dành cho bạn.
Overview
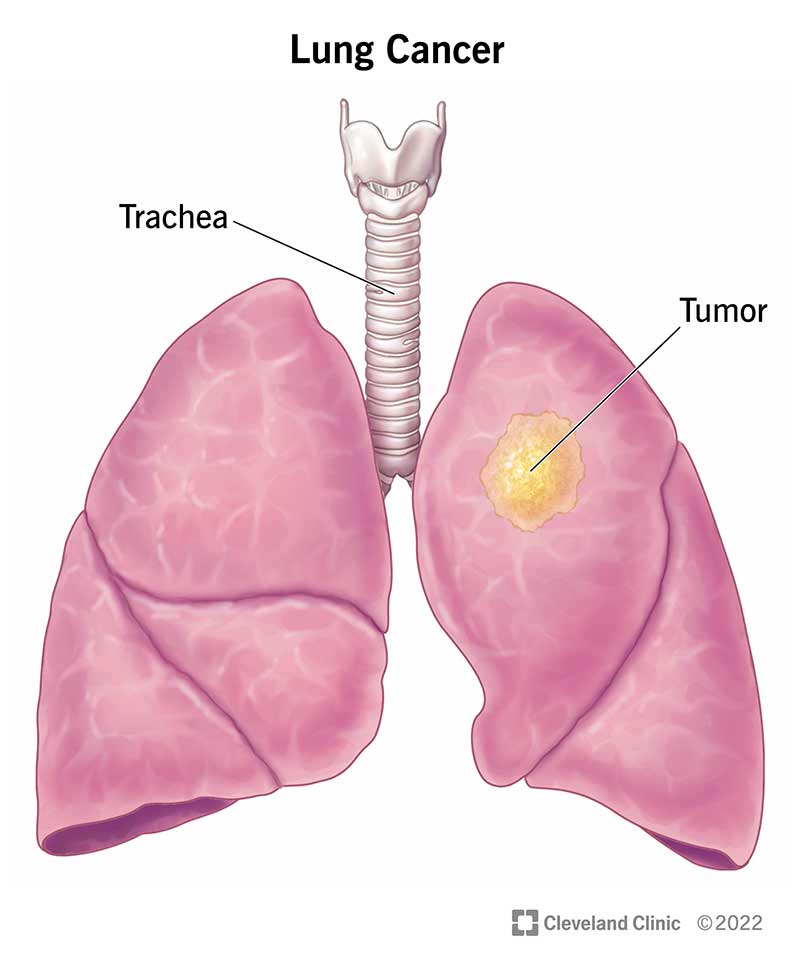
What is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is a disease caused by uncontrolled cell division in your lungs. Your cells divide and make more copies of themselves as a part of their normal function. But sometimes, they get changes (mutations) that cause them to keep making more of themselves when they shouldn’t. Damaged cells dividing uncontrollably create masses, or tumors, of tissue that eventually keep your organs from working properly.
Lung cancer is the name for cancers that start in your lungs — usually in the airways (bronchi or bronchioles) or small air sacs (alveoli). Cancers that start in other places and move to your lungs are usually named for where they start (your healthcare provider may refer to this as cancer that’s metastatic to your lungs).
What are the types of lung cancer?
There are many cancers that affect the lungs, but we usually use the term “lung cancer” for two main kinds: non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer. It accounts for over 80% of lung cancer cases. Common types include adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Adenosquamous carcinoma and sarcomatoid carcinoma are two less common types of NSCLC.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) grows more quickly and is harder to treat than NSCLC. It’s often found as a relatively small lung tumor that’s already spread to other parts of your body. Specific types of SCLC include small cell carcinoma (also called oat cell carcinoma) and combined small cell carcinoma.
Other types of cancer in the lungs
Other types of cancer can start in or around your lungs, including lymphomas (cancer in your lymph nodes), sarcomas (cancer in your bones or soft tissue) and pleural mesothelioma (cancer in the lining of your lungs). These are treated differently and usually aren’t referred to as lung cancer.
What are the stages of lung cancer?
Cancer is usually staged based on the size of the initial tumor, how far or deep into the surrounding tissue it goes, and whether it’s spread to lymph nodes or other organs. Each type of cancer has its own guidelines for staging.
Lung cancer staging
Each stage has several combinations of size and spread that can fall into that category. For instance, the primary tumor in a Stage III cancer could be smaller than in a Stage II cancer, but other factors put it at a more advanced stage. The general staging for lung cancer is:
- Stage 0 (in-situ): Cancer is in the top lining of the lung or bronchus. It hasn’t spread to other parts of the lung or outside of the lung.
- Stage I: Cancer hasn’t spread outside the lung.
- Stage II: Cancer is larger than Stage I, has spread to lymph nodes inside the lung, or there’s more than one tumor in the same lobe of the lung.
- Stage III: Cancer is larger than Stage II, has spread to nearby lymph nodes or structures or there’s more than one tumor in a different lobe of the same lung.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to the other lung, the fluid around the lung, the fluid around the heart or distant organs.
Limited vs. extensive stage
While providers now use stages I through IV for small cell lung cancer, you might also hear it described as limited or extensive stage. This is based on whether the area can be treated with a single radiation field.
- Limited stage SCLC is confined to one lung and can sometimes be in the lymph nodes in the middle of the chest or above the collar bone on the same side.
- Extensive stage SCLC is widespread throughout one lung or has spread to the other lung, lymph nodes on the opposite side of the lung, or to other parts of the body.
What is metastatic lung cancer?
Metastatic lung cancer is cancer that starts in one lung but spreads to the other lung or to other organs. Metastatic lung cancer is harder to treat than cancer that hasn’t spread outside of its original location.
How common is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is the third most common cancer in the U.S. Health systems report over 200,000 new cases of lung cancer each year.
